Antarctic Expedition Discovers New Patterns Under Glacier, Revealing New Melting Insights
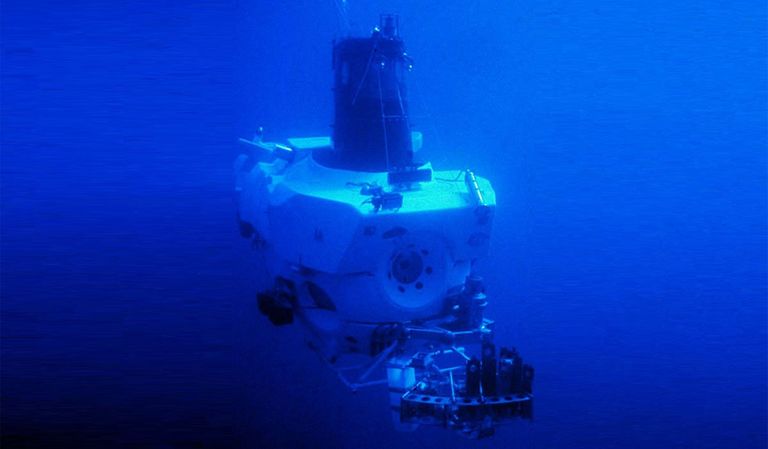
In 2022, scientists embarked on a groundbreaking expedition to study the Dotson Ice Shelf in West Antarctica. Using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), they discovered unusual teardrop shapes beneath the ice.
This expedition aimed to create the most detailed picture of the glacier’s underside ever.
Uncovering Teardrop Patterns
The ROV dove 10 miles under the Dotson Ice Shelf and traveled over 600 miles along its underside.

Source: Imgur
Unexpectedly, the team found teardrop shapes up to 1,300 feet long, which they believe are caused by uneven melting and Earth’s rotational forces.
The Role of Coriolis Force
These teardrop patterns are asymmetrical due to the Coriolis force, which affects water movement on Earth.

Source: Wikimedia
As water moves across the glacier’s underside, it creates a spiral flow pattern known as an Ekman spiral, typically seen when winds travel over surface water.
Significance of Dotson Ice Shelf
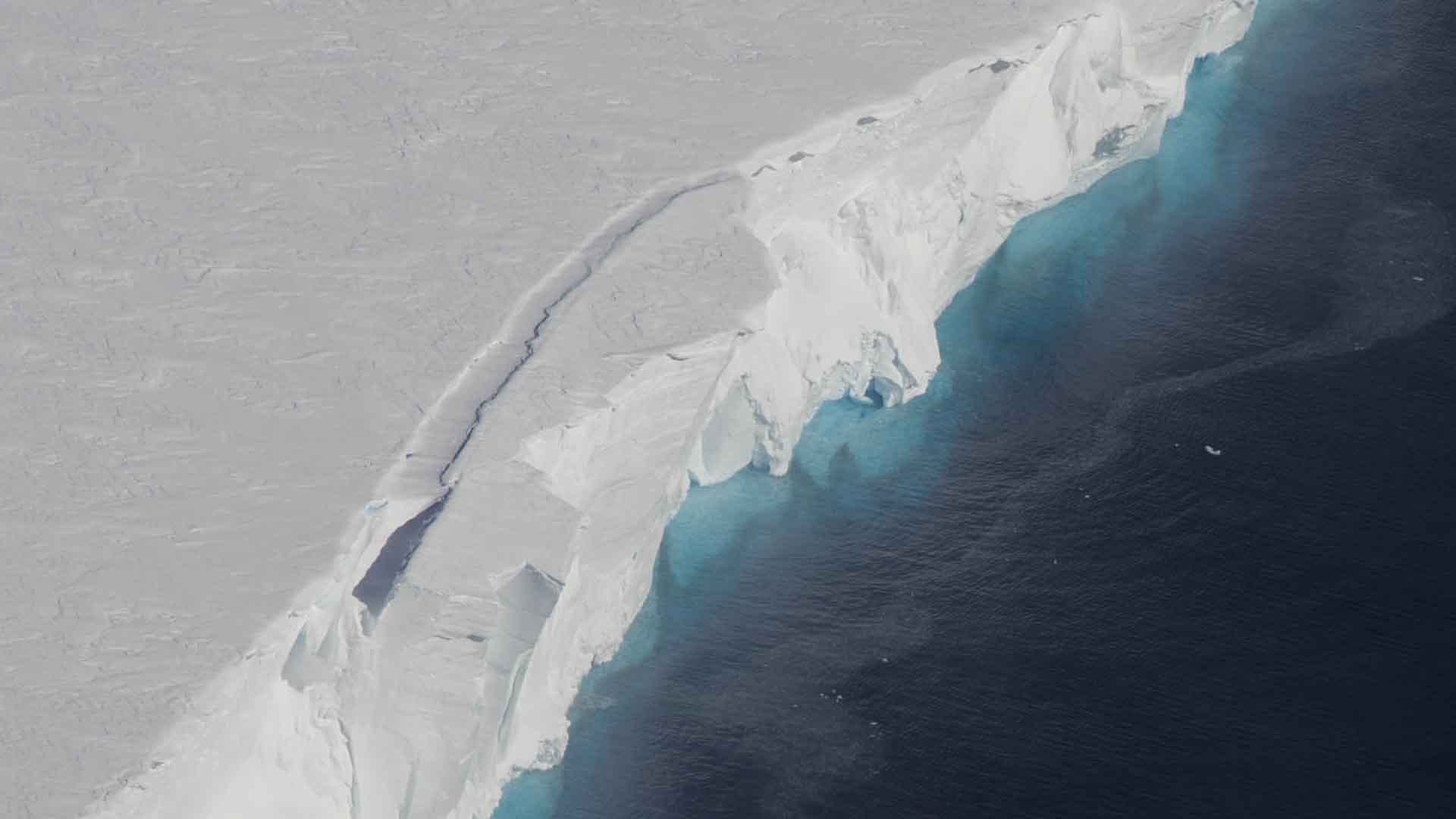
The Dotson Ice Shelf, a 30-mile-wide floating ice mass, is part of the larger West Antarctic ice sheet.

Source: NASA/Jeremy Harbeck
This ice sheet has the potential to cause a significant rise in sea levels, making its study crucial for understanding global climate impacts.
Threats to the Ice Shelf
Warm ocean water infiltrates the undersides of the ice shelf, unpinning it from the land.

Source: Jeremy Bishop/Pexels
Steady erosion is gradually wearing away at the edges, signaling that the eventual collapse of the ice shelf is not just possible — it’s inevitable.
Detailed Survey Findings
The survey revealed that the glacier is melting fastest at points where underwater currents erode its base.

Source: Melissa Bradley/unsplash
Fractures running through the glacier help the melt travel up to the surface, providing valuable insights into the melting process.
Unexpected Discoveries
While the team expected to see erosion patterns, the discovery of teardrop shapes was a surprise.

Source: henrique setim/Unsplash
These shapes are up to 1,300 feet long and are formed by the interaction of water movement and the glacier’s underside.
Ekman Spiral and Ice Melting
The Ekman spiral, as mentioned usually observed with winds over water, was identified in the water traveling over ice.

Source: Cassie Matias/Unsplash
This spiral flow pattern adds a new dimension to understanding how water movement affects ice melting in Antarctica.
Continuing the Research
In January 2024, the researchers returned with the ROV for further investigation. Unfortunately, the submersible was lost beneath the ice shelf, posing a new challenge for the team.
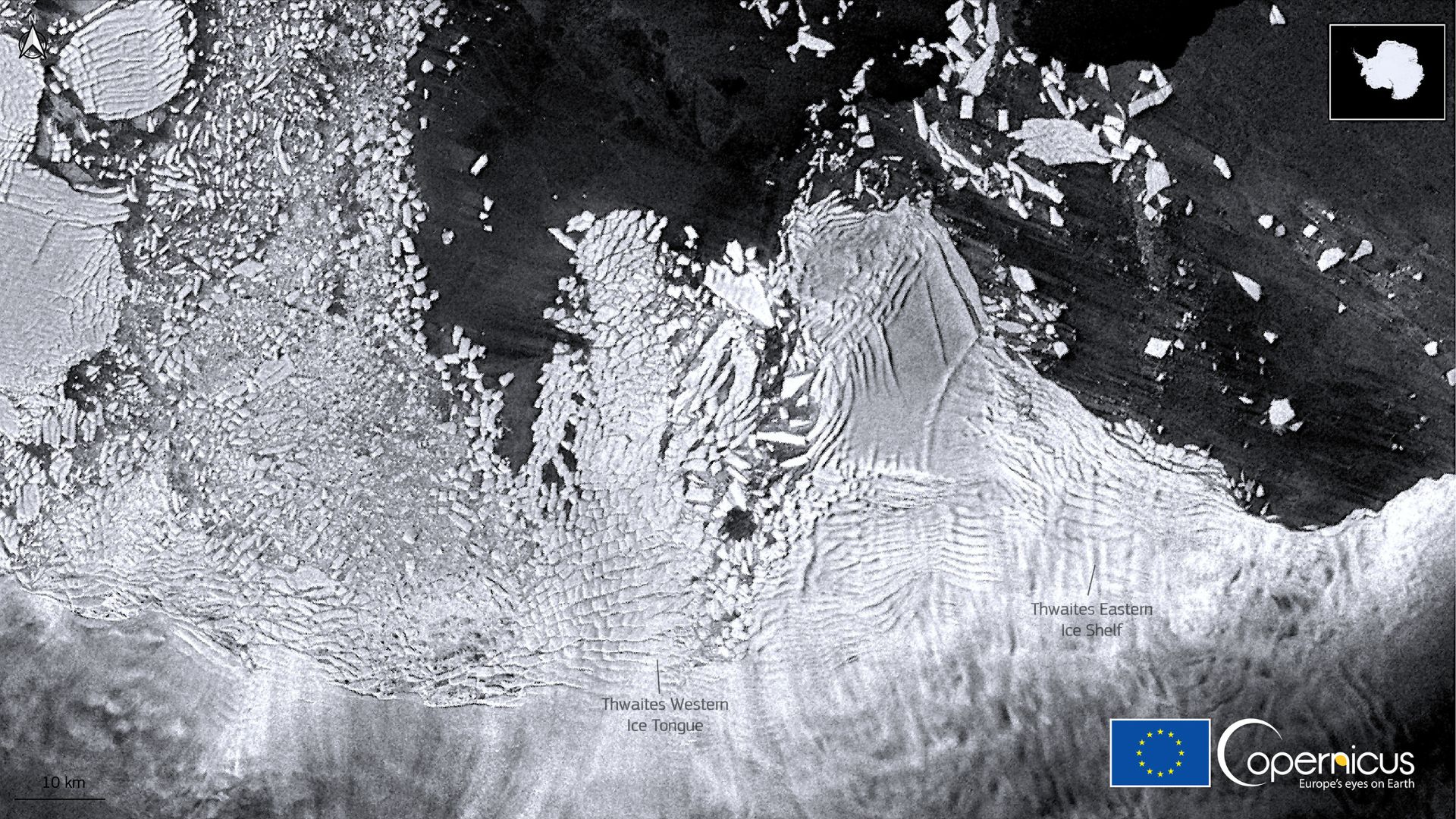
Source: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data 2021/Wikimedia Commons
Their goal is to continue exploring the uncharted depths.
Importance of Antarctic Ice
Professor Anna Wåhlin emphasized the critical role of Antarctic ice in stabilizing Earth’s temperature.

Source: Wikimedia
“All the ice in Antarctica is like a giant temperature stabilizer and an important part of Earth’s climate system,” she said.
Potential Impact on Sea Levels
Understanding the melting dynamics of the Antarctic ice sheet is crucial for predicting future sea level rise.

Source: Wikimedia
If the ice sheet melts at high rates, it can significantly influence sea levels globally, resulting in flooding and displacement of coastal communities
Future Expeditions
The research team plans to return with a new sub to continue their survey.
Source: Sean Gallup/Getty Images
Their findings will help set upper and lower limits on future sea level rise, providing essential data for climate scientists worldwide.
