China’s Space Program Makes Waves with Discovery of Water in Moon Soil
China has been investing heavily in its space program, aiming to catch up with traditional space powers like the United States and Russia.
Over the past decade, China has launched several successful lunar missions, each pushing the boundaries of space exploration.
The Chang'e-5 Mission
In 2020, China’s Chang’e-5 mission made history by being the first mission in four decades to return with lunar samples.

Source: Wikimedia
The rover brought back rock and soil samples from a high-latitude region of the moon, providing new data for scientists to analyze.
Discovery of Water in Moon Soil
Scientists from Chinese universities analyzing the Chang’e-5 samples found traces of water.

Source: Freepik
This discovery was significant as the samples were from a much higher latitude than previous missions, offering new insights into the presence and form of water on the moon.
Hydrated Salts in Sunlit Areas
The samples revealed that water molecules can persist in sunlit areas of the moon in the form of hydrated salts.

Source: Christian Bass/Unsplash
The finding was detailed in the journal Nature Astronomy, providing a fresh perspective on lunar water’s chemical and physical forms.
Unknown Lunar Mineral
The Chang’e-5 samples also contained a new mineral crystal, dubbed “unknown lunar mineral (ULM-1)”, which is rich in water and ammonia molecules.

Source: Wikimedia
Over 40 percent of this mineral by mass is composed of water, making it a significant discovery for future lunar exploration, as well as providing potential insights into the moon’s origin and evolution.
Ruling Out Contamination
Researchers ensured the integrity of their findings by ruling out terrestrial contamination or rocket exhaust as sources of the detected water.

Source: Freepik
The chemical and isotopic compositions of the samples confirmed their lunar origin.
Implications for Future Missions
The presence of water on the moon has far-reaching implications for future space missions.

Source: NASA/Unsplash
Water can be used to produce rocket fuel and support human life, making long-term lunar missions more feasible and sustainable.
China's Space Achievements
China’s space achievements go beyond the Chang’e-5 mission.
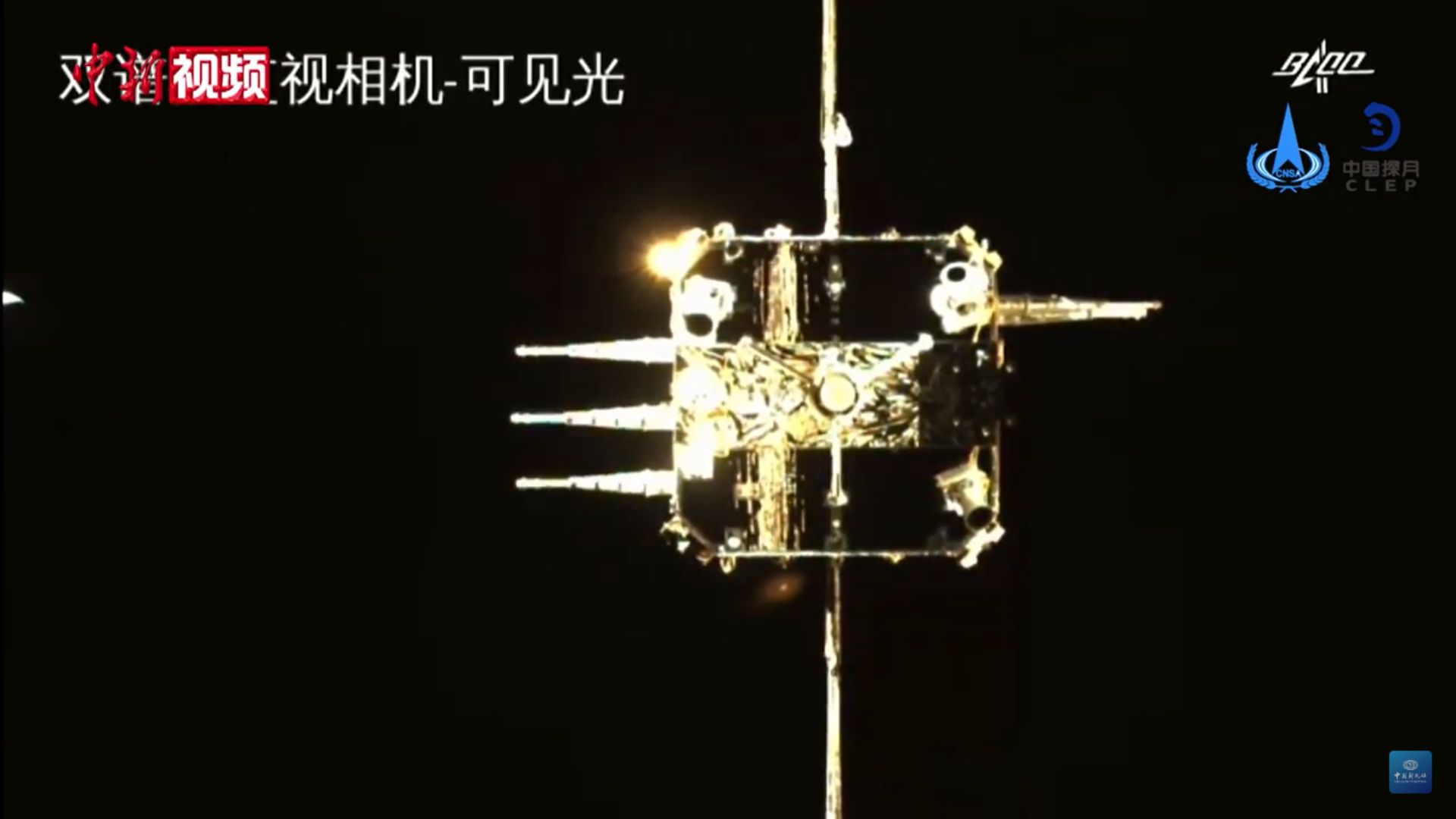
Source: China News Service/Wikimedia Commons
In January 2019, the Chang’e-4 mission made a historic landing on the far side of the moon, and the recent Chang’e-6 mission brought back the first samples from this unexplored region.
Competing in the New Space Race
China’s space program is seen as a major competitor in the new space race.

Source: NASA
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson has noted the competitive nature of this era, with China’s rapid advancements posing a significant challenge to the United States.
Plans for a Lunar Base
China has ambitious plans to send a crewed mission to the moon by 2030 and aims to build a lunar base.

Source: NASA/Newsmaker/Getty Images
These goals highlight China’s commitment to establishing a long-term presence on the moon.
Understanding Lunar History
Finding water on the moon is not just about resources for space missions.
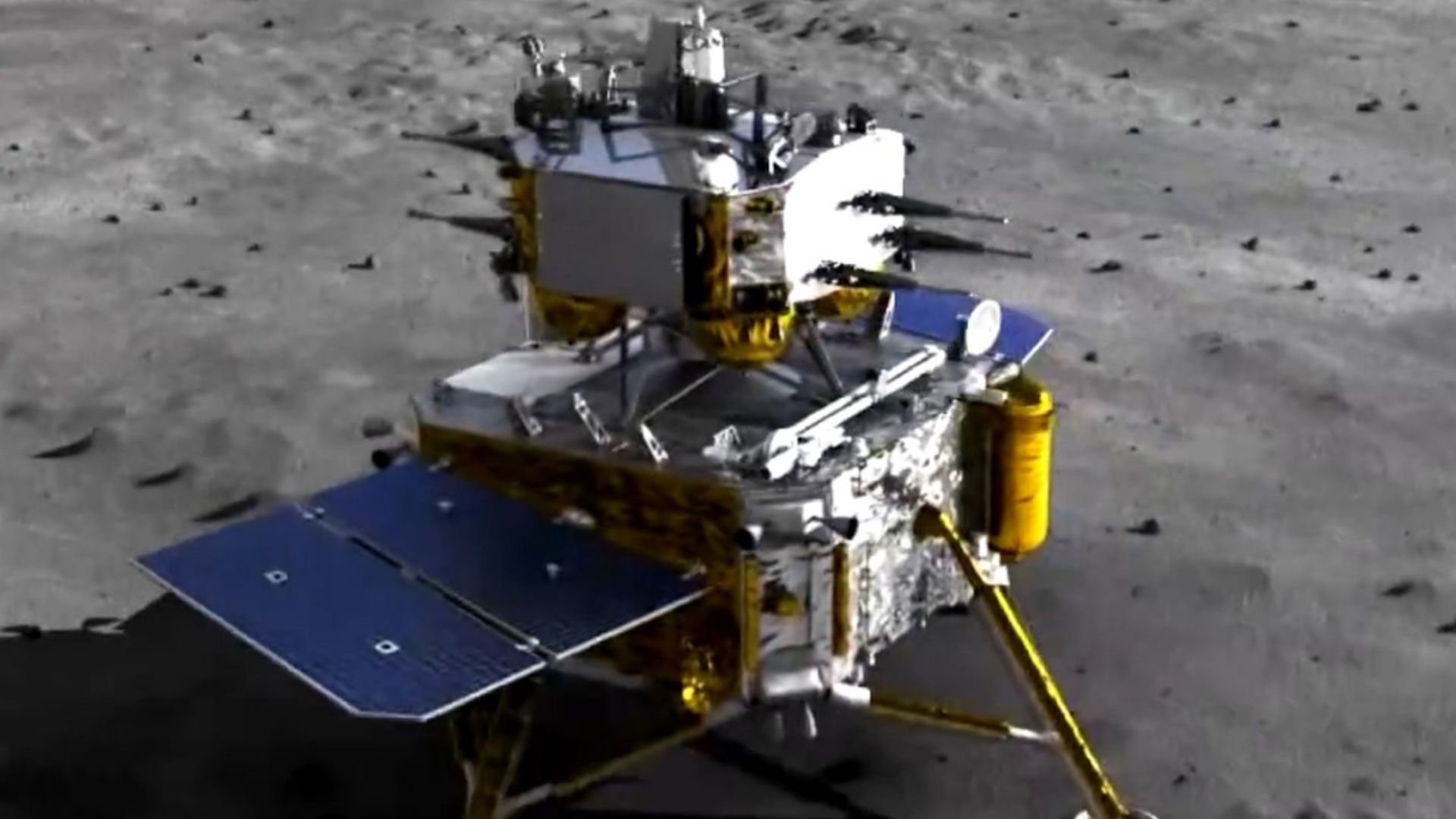
Source: China News Service/Wikimedia Commons
It also provides new insights into the moon’s geological history and evolution, potentially reshaping our understanding of its formation.
A New Era of Exploration
China’s discovery of water in lunar soil marks a new era of exploration and discovery.
Source: NASA/Interim Archives/Getty Images
As China continues to push the boundaries of space exploration, these findings will play a crucial role in shaping the future of lunar and space missions.
