Earth Dodges Solar Flare Bullet – Another Powerful Eruption Follows Historic Solar Storm
The sun has been particularly active lately, emitting powerful solar flares. On Tuesday, it released another significant flare, just a week after a severe solar storm.
This recent activity has scientists and space weather enthusiasts on high alert, as the sun’s 11-year solar cycle reaches its peak.
Largest Solar Flare Since 2017
The latest solar flare is the largest detected since 2017. Classified as an X-8.7 magnitude, it surpasses the strength of previous flares.
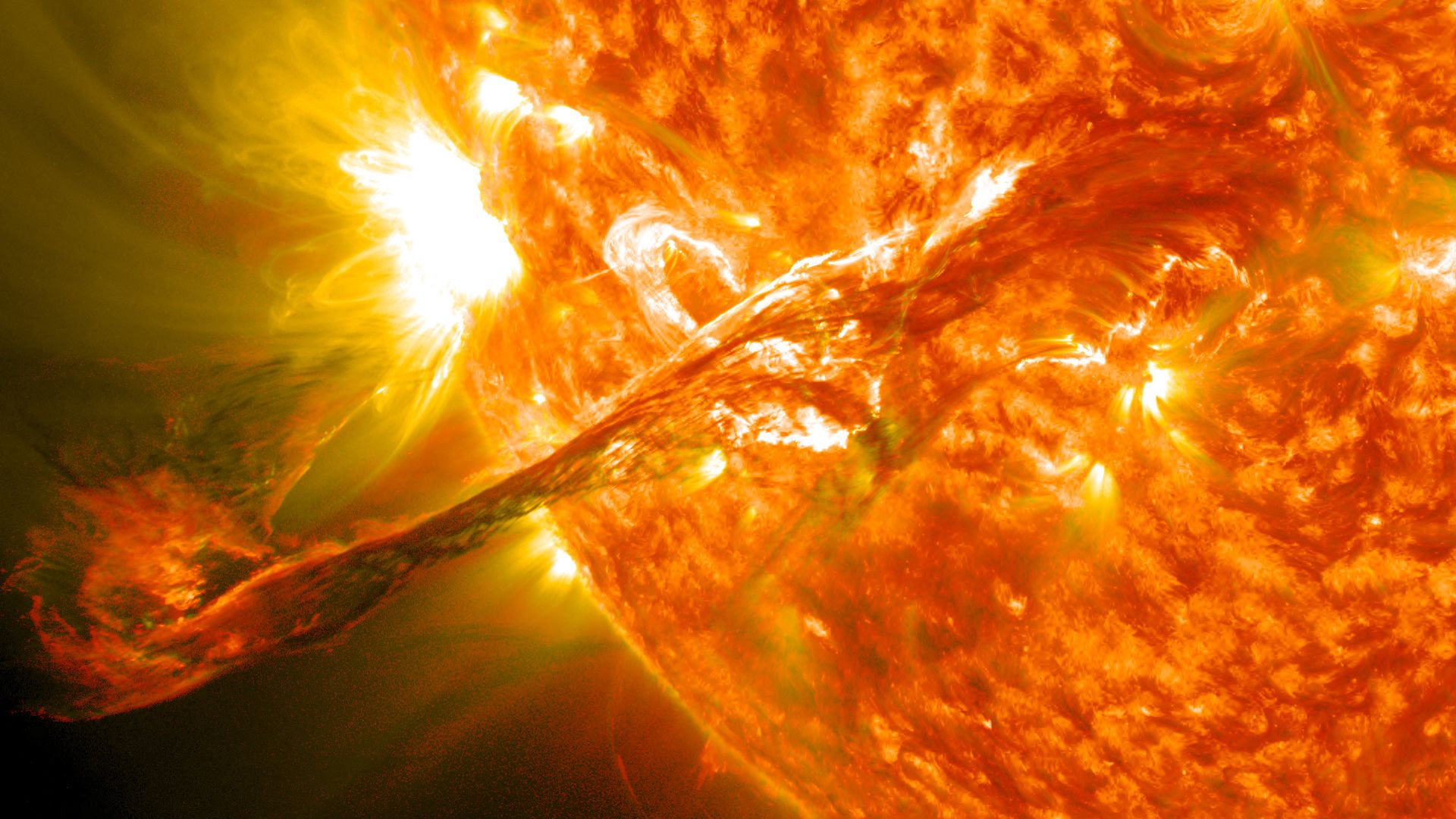

Source: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center/Wikimedia Commons
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) confirmed this flare as the biggest of the current solar cycle, emphasizing the increasing solar activity.
Understanding Solar Flares
Solar flares are intense bursts of radiation caused by magnetic energy from sunspots. They can last from a few minutes to several h
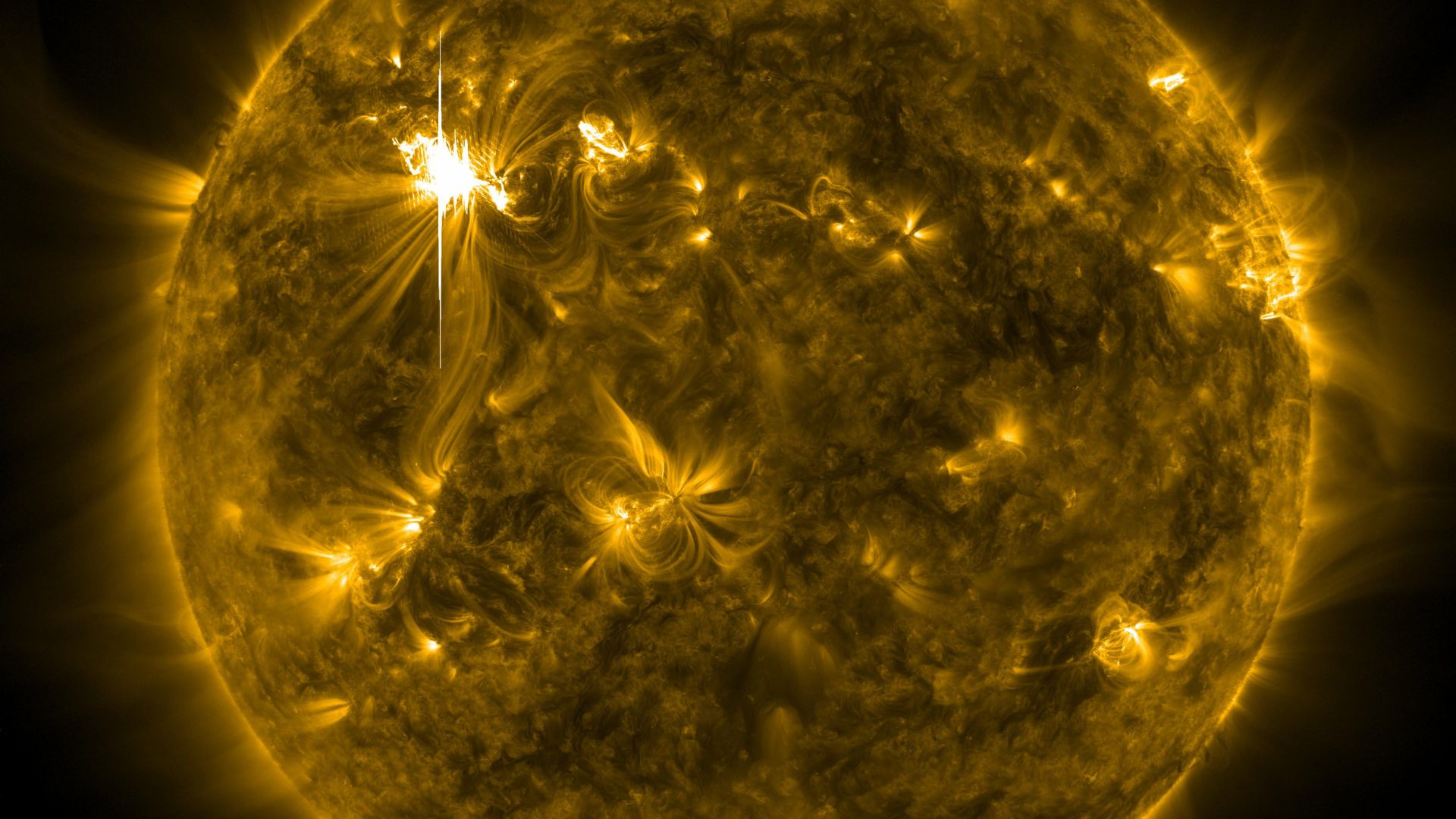
Source: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center/Wikimedia Commons
NASA classifies these flares from B-class, the smallest, to X-class, the largest. Each class represents a ten-fold increase in energy, with X-class flares being the most powerful.
Impact on Earth’s Technology
Powerful solar flares can disrupt radio communications, electric power grids, and GPS signals. The recent solar storm caused some power grid irregularities and interfered with GPS signals, even affecting farming equipment.

Source: Freepik
Such disruptions highlight the importance of monitoring solar activity closely.
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured images of the recent flare, which peaked at around 12:51 p.m. ET.

Source: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio - A. J. Christensen, Scott Wiessinger/Wikimedia Commons
The SDO plays a crucial role in observing the sun, providing valuable data to help predict and understand solar events. This data is essential for preparing and mitigating potential impacts on Earth.
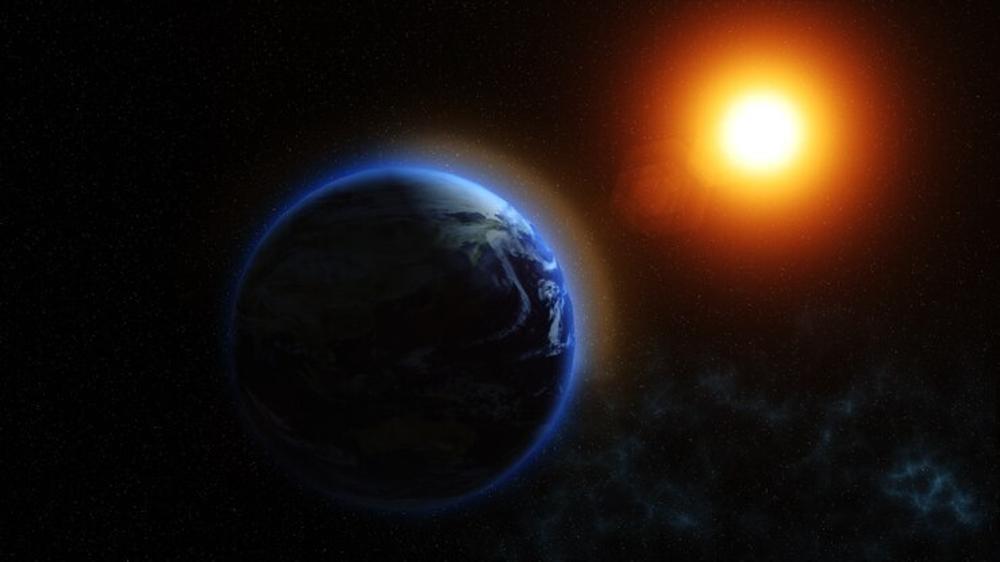
Geomagnetic Storms and Auroras
The solar storm from the previous week sent coronal mass ejections (CMEs) toward Earth, creating a powerful geomagnetic storm.

Source: Dwxn/Wikimedia Commons
This storm produced stunning northern lights, visible in regions not typically known for aurora sightings. Such events offer a beautiful but potentially disruptive spectacle.
Potential Threats from Solar Activity
While the recent X-class flare occurred on the sun’s western side, away from Earth, it still posed a risk of temporarily disrupting high-frequency radio signals.
International Gemini Observatory/Wikimedia Commons
NOAA issued warnings, underscoring the need for vigilance as solar activity increases towards the solar maximum expected in 2025.
Protecting Our Technology
With increasing solar activity, protecting satellites and other technologies becomes crucial. Enhanced monitoring and prediction capabilities are being developed to provide accurate forecasts and timely warnings.
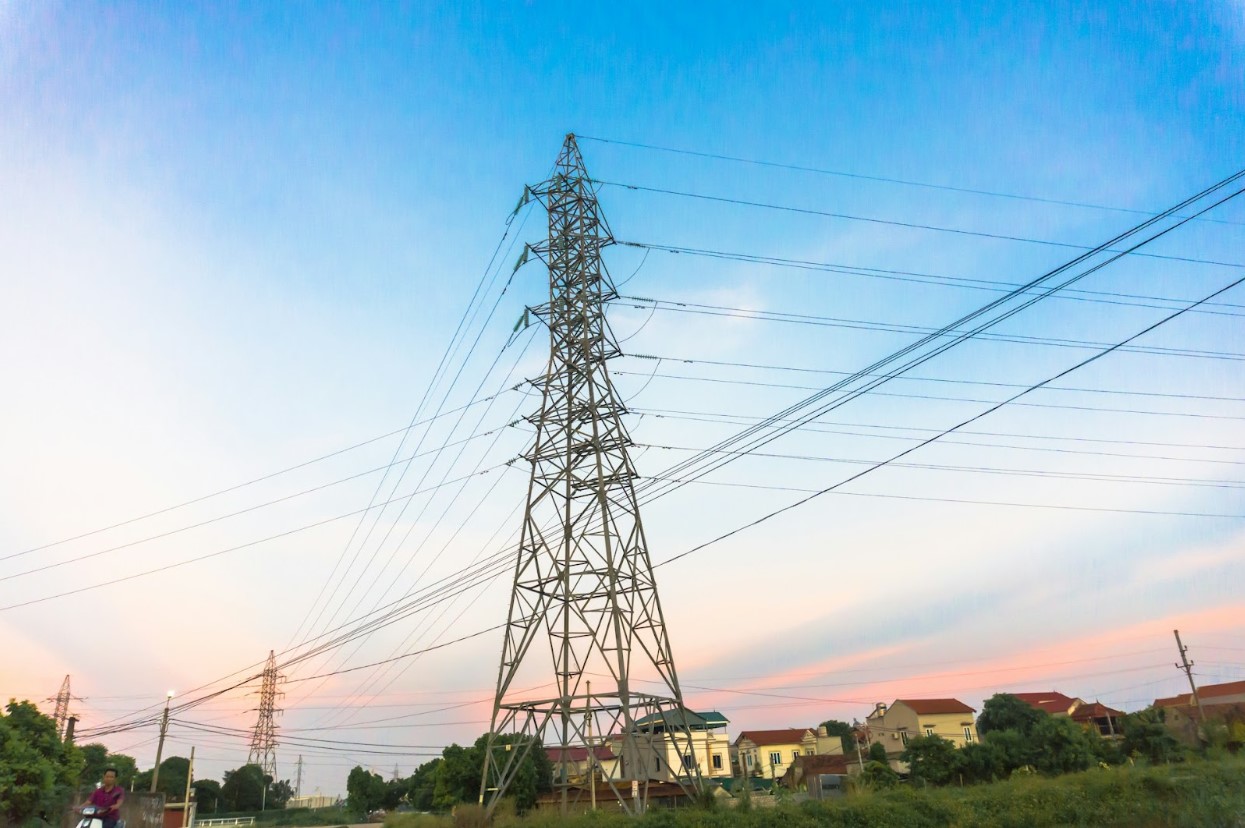

Source: Leohoho/Unsplash
These efforts are essential for safeguarding critical infrastructure and ensuring the continuity of essential services.
International Collaboration in Space Weather Research
Space weather research is a global effort. International collaboration between space agencies, research institutions, and private companies is vital.

Source: Wikimedia
By working together, we can advance our understanding and preparedness, minimizing the impacts of solar events on our technology and daily lives.
Future Solar Maximum Predictions
Solar flares and storms are expected to become more frequent by 2025, as the sun reaches its solar maximum. Scientists predict increased solar activity, necessitating continuous monitoring and research.
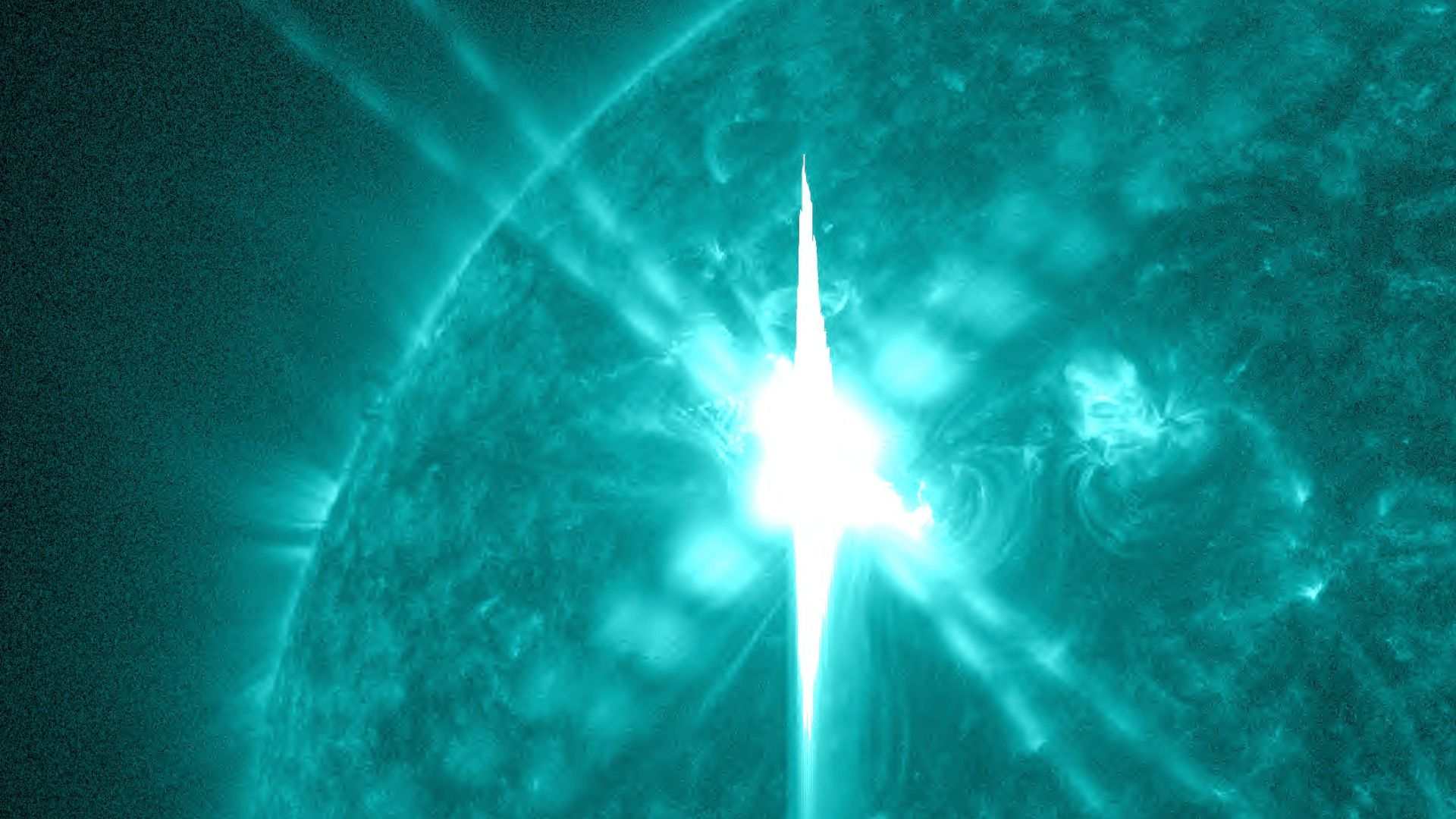
Source: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center/Wikimedia Commons
Understanding the sun’s behavior helps us prepare for future solar events and their potential impacts.
Quotes from NOAA and NASA
NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center emphasized, “Not done yet!” in a social media post, reflecting the ongoing solar activity.

Source: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center/Wikimedia Commons
NASA’s observations and data collection are crucial for predicting and understanding these events. Both agencies play a key role in monitoring and mitigating the effects of solar flares.
Staying Prepared
As solar activity intensifies, staying informed and prepared is essential. By understanding the potential impacts of solar flares and taking proactive measures, we can mitigate risks and appreciate the natural beauty of events like the northern lights.

Source: Wikimedia
Awareness and preparedness are key to navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by our dynamic sun.
