NASA Spots Unknown Luminous Shapes Wandering in Earth’s Atmosphere
NASA’s latest satellite observations have uncovered peculiar X- and C-shaped patterns within Earth’s ionosphere, a crucial layer of charged gas that facilitates long-distance radio communication.
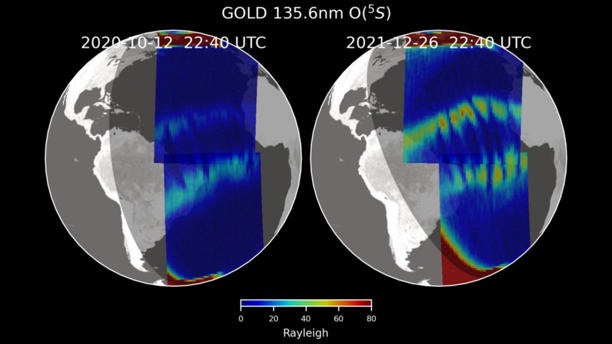
The discovery, made by the Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) mission, reveals how various factors can cause disturbances in this atmospheric layer. These unexpected alphabetical patterns emerged even in the absence of clear atmospheric disturbances.
Unexpected Findings During Quiet Conditions
Fazlul Laskar from the University of Colorado, the lead author of the study, expressed surprise at the findings, stating in a NASA press release, “Earlier reports of merging were only during geomagnetically disturbed conditions. It was an unexpected feature during geomagnetic quiet conditions.”

Source: Ethan Miller/Getty Images
NASA’s Jeffrey Klenzing also noted, “The X is odd because it implied that there were far more localized driving factors. This was expected during extreme events, but seeing it during ‘quiet time’ suggested that the lower atmosphere’s activity significantly influenced the ionospheric structure.”
Discovery of C-Shaped Bubbles
Knewz.com reported that the mission identified C-shaped bubbles in the ionospheric plasma, alongside the X-shaped patterns. These C-shaped bubbles were found unusually close to one another, a phenomenon scientists initially attributed to changes in wind direction.
Source: NASA
However, observing C and reverse-C shapes just 400 miles (643 kilometers) apart was unusual, as wind patterns generally do not fluctuate so drastically over such short distances.
Concerns About Plasma Distortion
LASP research scientist Deepak Karan, who authored a separate paper published in November in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, emphasized the importance of understanding these phenomena.

Source: Wikimedia
Karan remarked, “It was really important to find out why this was happening. If a vortex or a very strong shear in the plasma had occurred, this would completely distort the plasma over that region. Signals would be lost completely with a strong disturbance like this.”
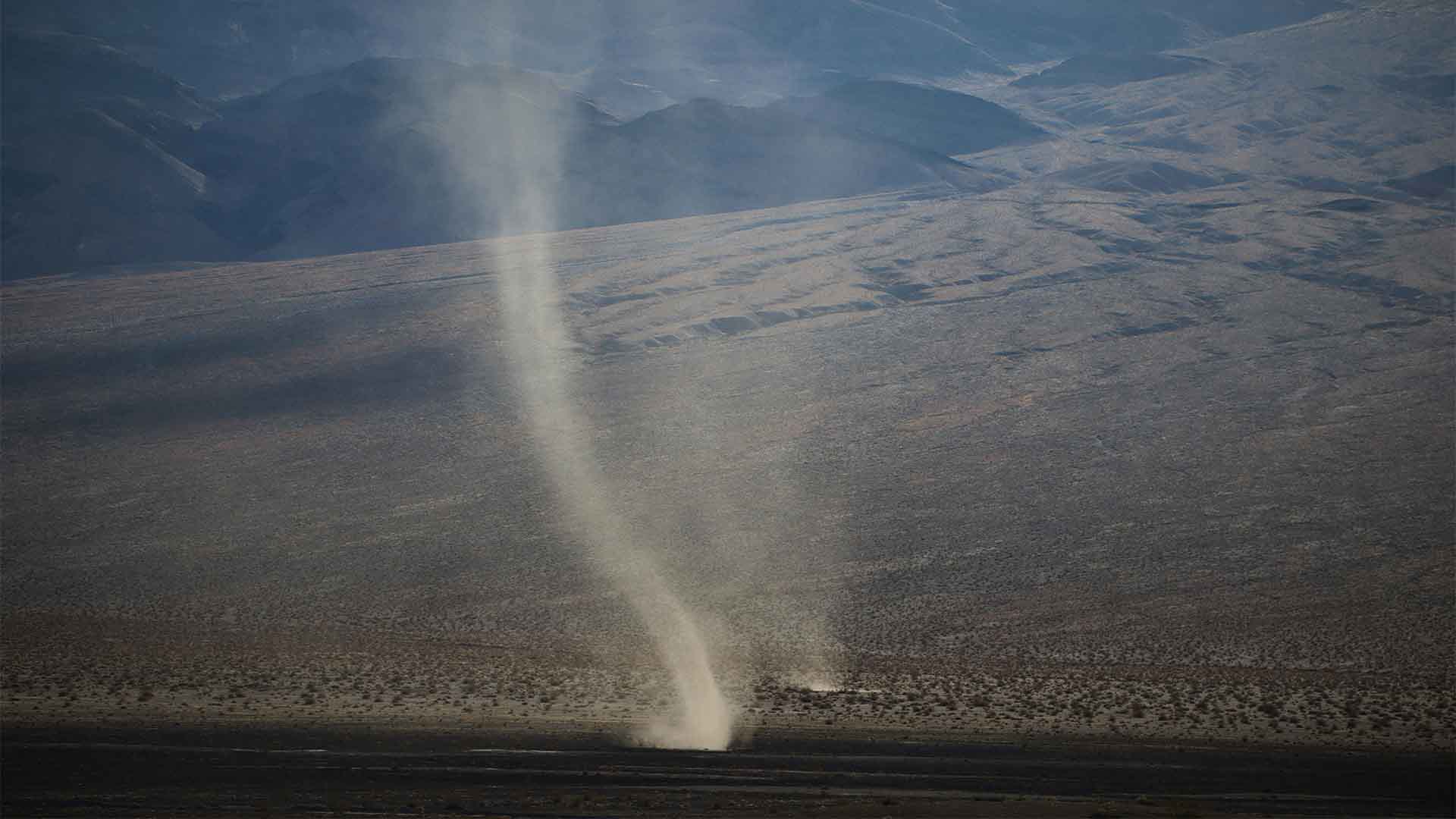
Comparison to Tornadoes and Dynamic Behavior
Karan further explained that these vortices, which can last for hours, are comparable to tornadoes in Earth’s lower atmosphere.

Source: Thilani Ratheep/Pexels
Scientists are particularly concerned about their formation in the ionosphere during calm periods. Laskar noted, according to LiveScience, “These shapes revealed that the ionosphere could be very dynamic at times, displaying unexpected structures. It also demonstrated that lower atmospheric weather could have a significant impact on the ionosphere.”
Role of the Ionosphere and Solar Influence
The ionosphere is a segment of Earth’s atmosphere energized by the sun’s radiation. Sunlight during the day charges molecules, transforming them into plasma that aids in long-distance radio transmission.

Source: Freepik
Besides sunlight, the ionosphere is influenced by solar storms and major volcanic eruptions. Since its launch in October 2018, NASA’s GOLD mission has been measuring the density and temperature of the ionosphere, yet many questions remain about how lower atmospheric changes and solar activity affect charged particles in this layer.
Previous NASA Efforts on Ionospheric Study
Prior to this, NASA had made efforts to understand the ionosphere’s complexities.

Source: Picryl
The Atmospheric Perturbations Around The Eclipse Path (APEP) project explored how variations in sunlight and temperature impact the upper atmosphere.
GOLD’s Contribution to Ionospheric Mysteries
Karan shared with CNN, “Due to GOLD’s wide view and continuous measurements, we were able to observe these mysteries within the ionosphere.”

Source: Wikimedia
This comprehensive observation capability has shed new light on previously elusive aspects of the ionosphere.
Impact on GPS and Satellite Communications
Laskar also discussed the implications for GPS and satellite communications, stating, “One of the challenges for ionospheric researchers was to eventually be able to predict its dynamics in advance so that we could be prepared for GPS signal loss and interruptions to satellite communications.”
Source: Mathieu Lewis-Rolland/Getty Images
The findings highlight the need for better predictive capabilities in managing these crucial technologies.
Ongoing Research and Future Implications
The ongoing research by NASA and other institutions continues to explore these unexpected ionospheric phenomena.

Source: Wikimedia
The insights gained from GOLD’s observations could lead to advances in understanding and predicting ionospheric behavior, with significant implications for communication and navigation technologies.
Broader Context of Ionospheric Studies
These discoveries contribute to a broader understanding of the ionosphere’s role in Earth’s atmosphere and its interaction with various factors.

Source: Freepik
By exploring these unexpected patterns, scientists are better positioned to address the challenges posed by dynamic atmospheric conditions.
Looking Ahead
As research into the ionosphere progresses, further observations and studies will be crucial in unraveling the complexities of this vital atmospheric layer.

Source: Alexander Gerst/ESA via Getty Images
The continued work of missions like GOLD promises to enhance our knowledge and improve our ability to manage and predict ionospheric behavior.
