Scientists Have Identified Ancient Stone Tools Found In Ukraine As Possibly the Oldest in Europe
A new research paper published in the journal Nature identifies ancient stone tools that may be the earliest evidence of humans living in Europe.
The tools may be 1 million or more years old and were found in the area of western Ukraine. Researchers used new dating methods to come to this conclusion, which may make the Ukraine archeological site important for future discoveries.
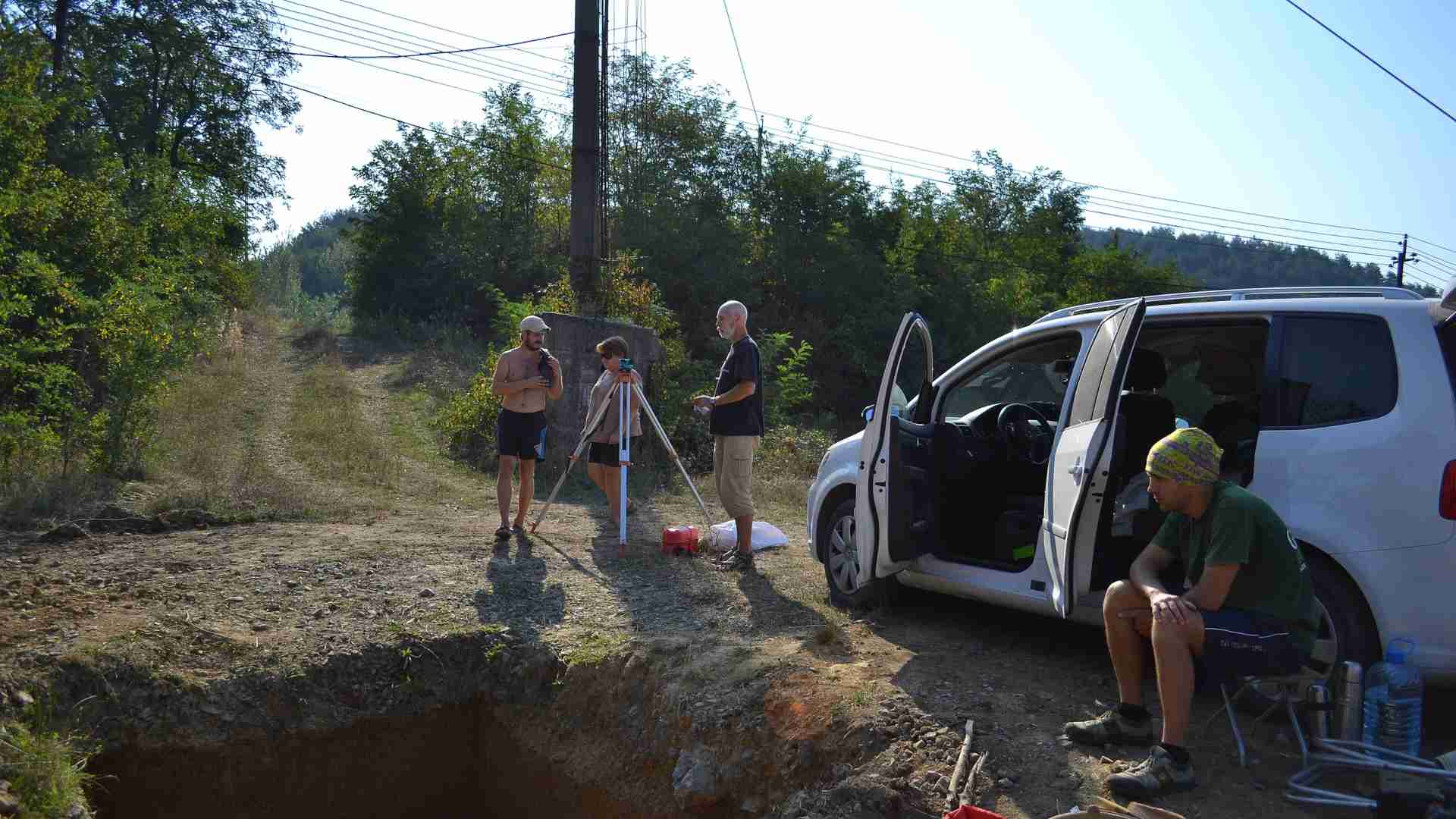
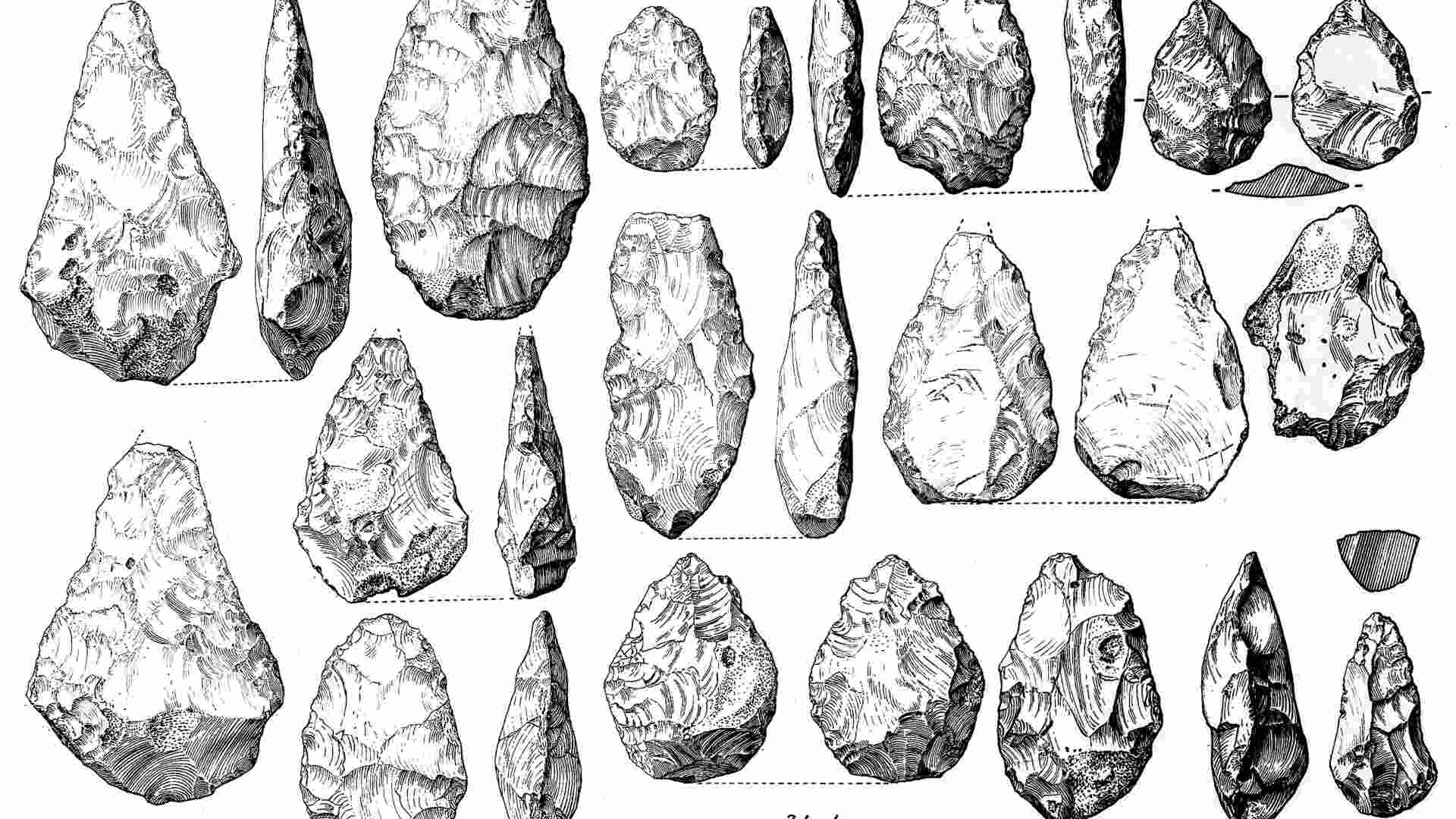
In their study, researchers identified a series of chipped stones excavated in Ukraine in the 1970s.

Source: Sochka Yaroslav/Wikimedia
Researchers determined that this series of stones, which may look like normal rocks to the untrained eye, were actually shaped by human hands a long time ago. The chipped stones were found in Korolevo, and its location is noteworthy because of how far north it is compared to other locations where tools have been found.
What are Chipped Stones?
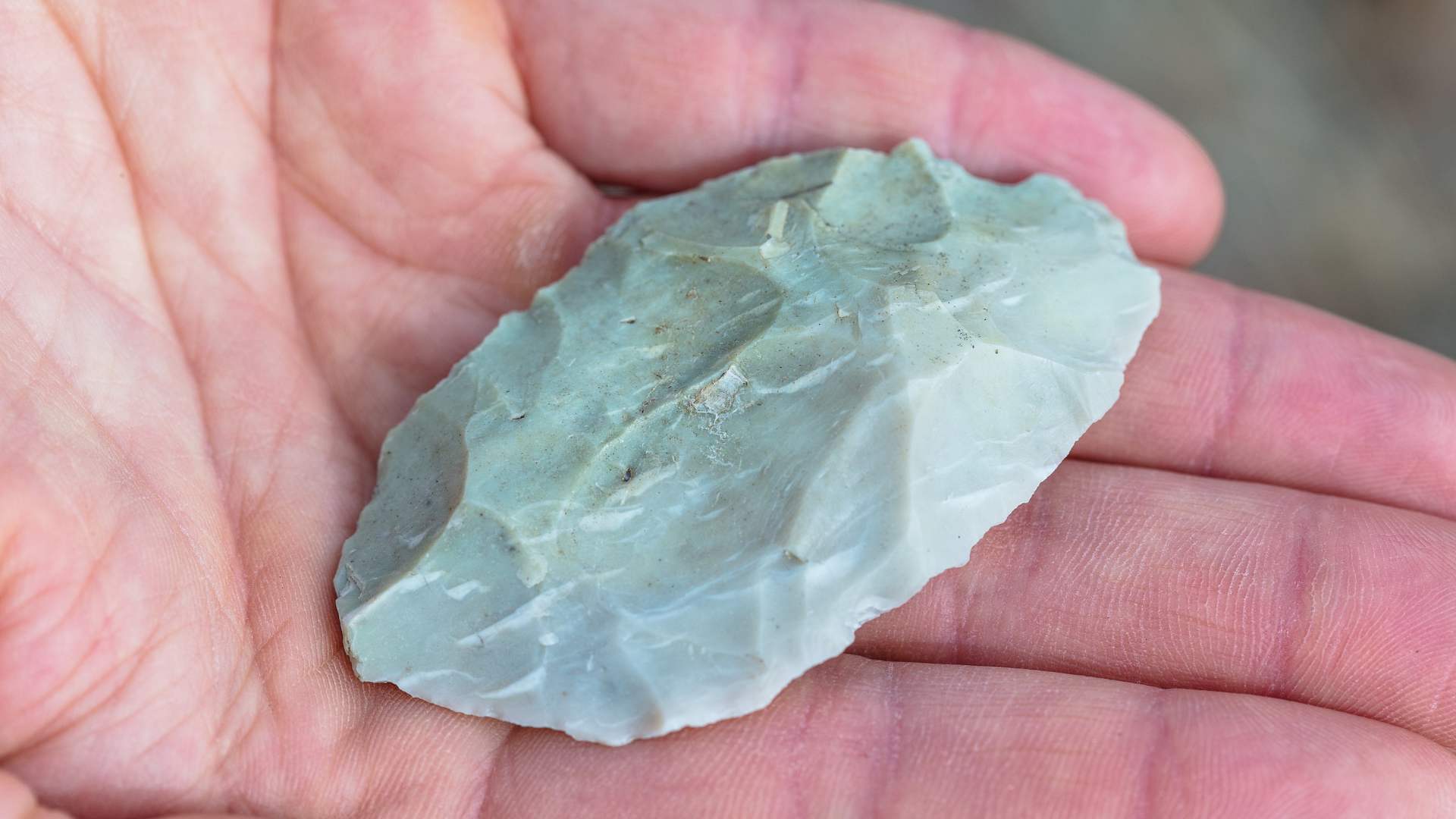
Chipped stones are a type of prehistoric tool that archaeologists think ancient humans used to assist them in their daily lives.

Source: Yellowstone National Park/Wikimedia
The earliest stone tools in the entire world that have been found are thought to have been used over 2 million years ago. Chipped stones had a variety of uses. They were used as blades to cut things, scrapers, or even sharp projectiles that could be thrown.
Chipped Stone Categories
Archaeologists classify chipped stone tools into distinct categories based on their usage. One type is known as arrowheads or projectile points. These were used for hunting and fighting other humans.
Source: Wikimedia
Another type is hand axes, which were used between 1.7 million and 100,000 years ago. There are also crescents that could be used both as blades or drills and often were used to make beads in the ancient world.
Other Types of Ancient Tools
While stone tools are the oldest surviving ones that we have from ancient humans, many others were used as well.

Source: José-Manuel Benito Alvarez/Wikimedia
Ancient humans commonly used bone and wood materials to make tools. Unfortunately, because of the passage of time, these organic type of materials did not survive to the present day. This leaves us researchers only with stone tools that they can directly analyze.
Age of the Tools
Researchers in the published Nature study used contemporary methods of sedimentary rock layer dating to determine that the tools found in Korolevo, Ukraine are over $1 million years old.
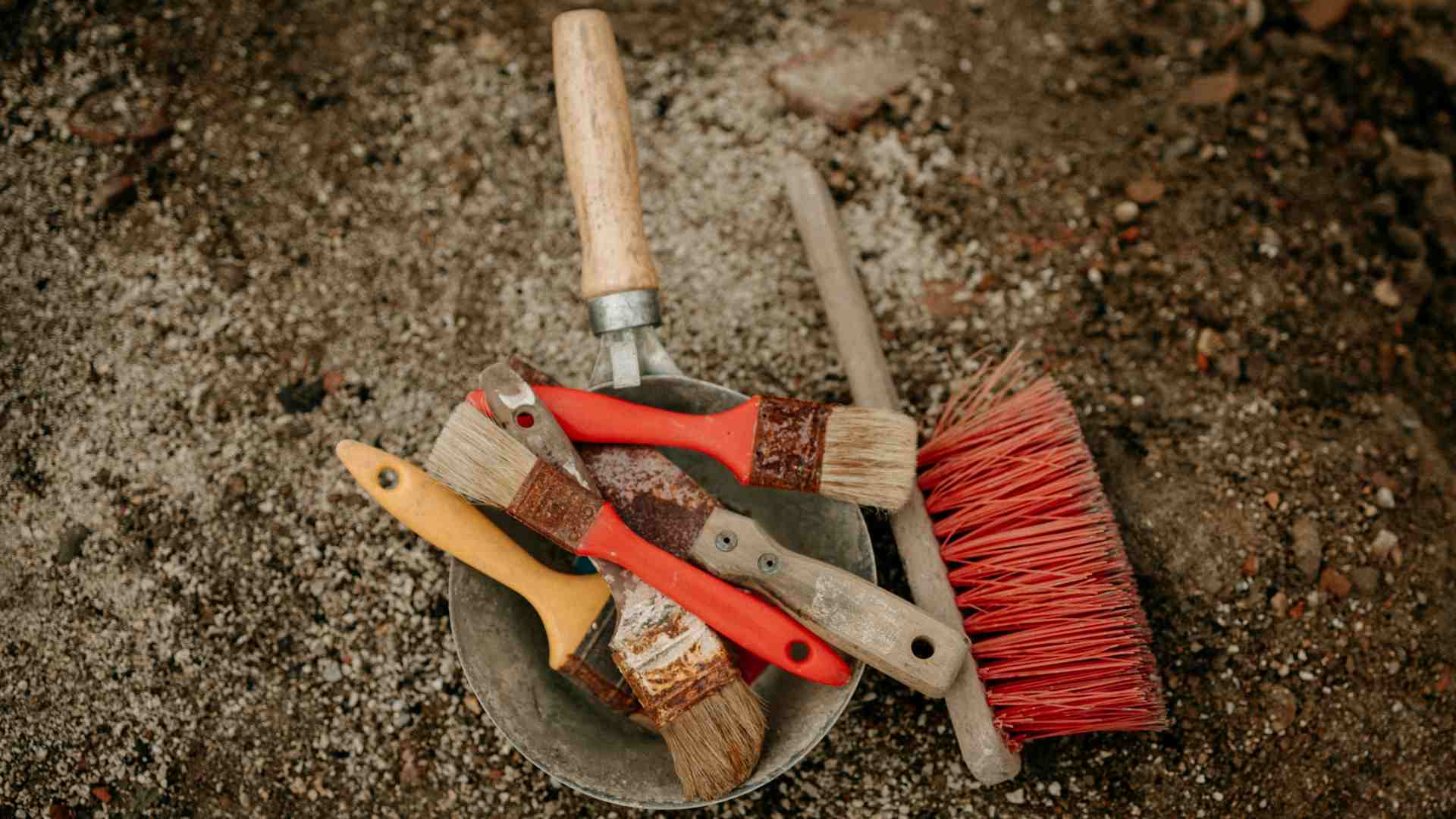

Source: Trnava Universty/Unsplash
“Here, using two methods of burial dating with cosmogenic nuclides we report ages of 1.42 ± 0.10 million years and 1.42 ± 0.28 million years for the sedimentary unit that contains Mode-1-type lithic artefacts,” said the study abstract.
Earliest Hominin Presence in Europe
An interesting and novel part of this new research is that the age of the tools creates evidence that humans existed in Europe at this early time.

Source: Ryan Somma/Wikimedia
“Korolevo represents, to our knowledge, the earliest securely dated hominin presence in Europe, and bridges the spatial and temporal gap between the Caucasus (around 1.85–1.78 million years ago) and southwestern Europe (around 1.2–1.1 million years ago)”
Advancing the East Colonization Hypothesis
The research team who conducted the study concluded that these recent findings provide evidence for a scientific hypothesis about how Europe came to be inhabited.
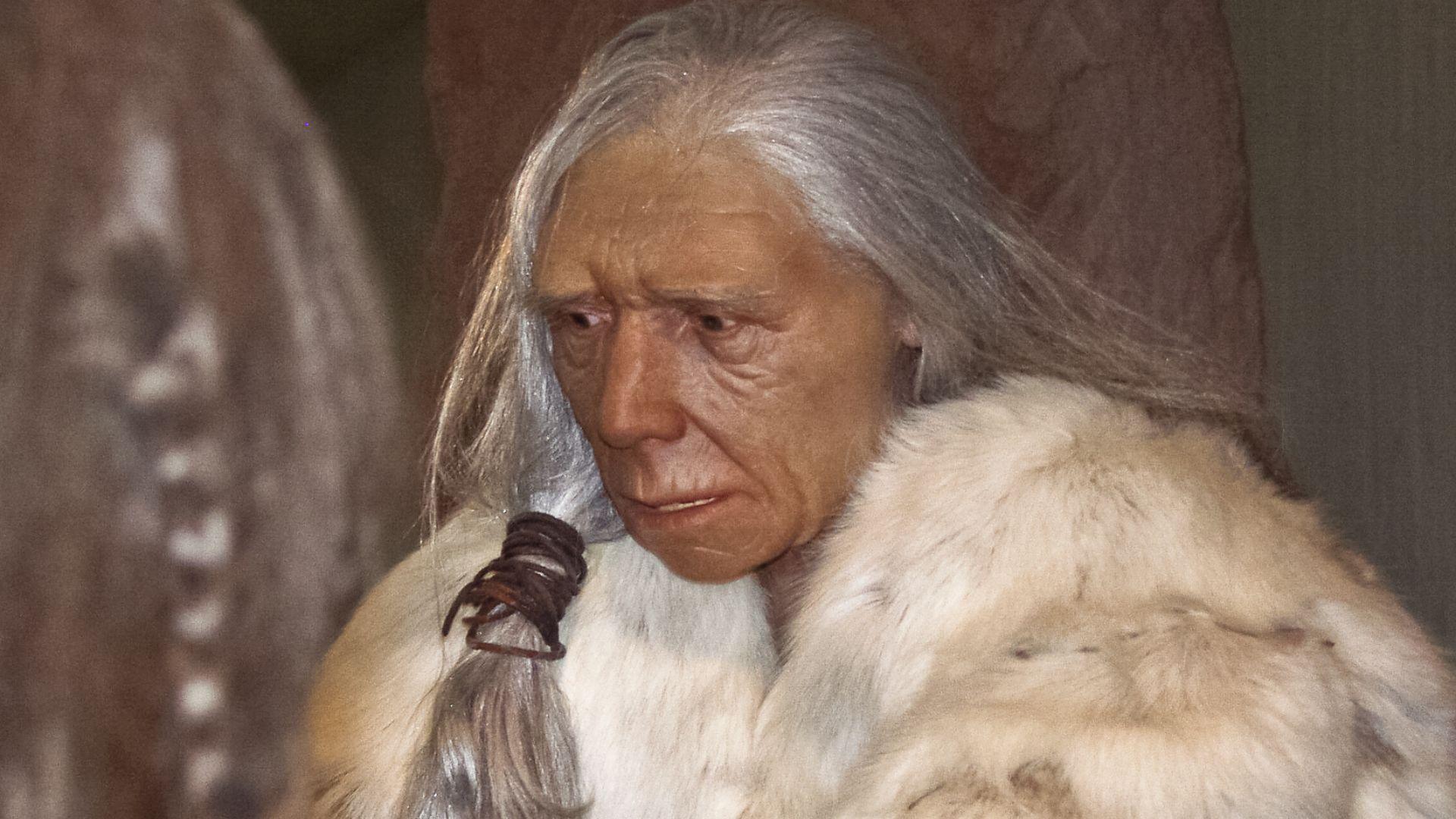

Source: Fährtenleser/Wikimedia Commons
“Our findings advance the hypothesis that Europe was colonized from the east, and our analysis of habitat suitability suggests that early hominins exploited warm interglacial periods to disperse into higher latitudes and relatively continental sites—such as Korolevo—well before the Middle Pleistocene Transition.”
It’s Unclear Which Ancient Humans Are Responsible
While the researchers were able to put dates to these stone tools, there are still questions about their use. For example, there hasn’t yet been a way to narrow down which types of ancient humans created the tools.

Source: Eunostos/Wikimedia Commons
Roman Garba, an archeologist and co-author of the study said “We don’t have fossil remains, so we can’t be sure.”
What Were These Tools Used For?
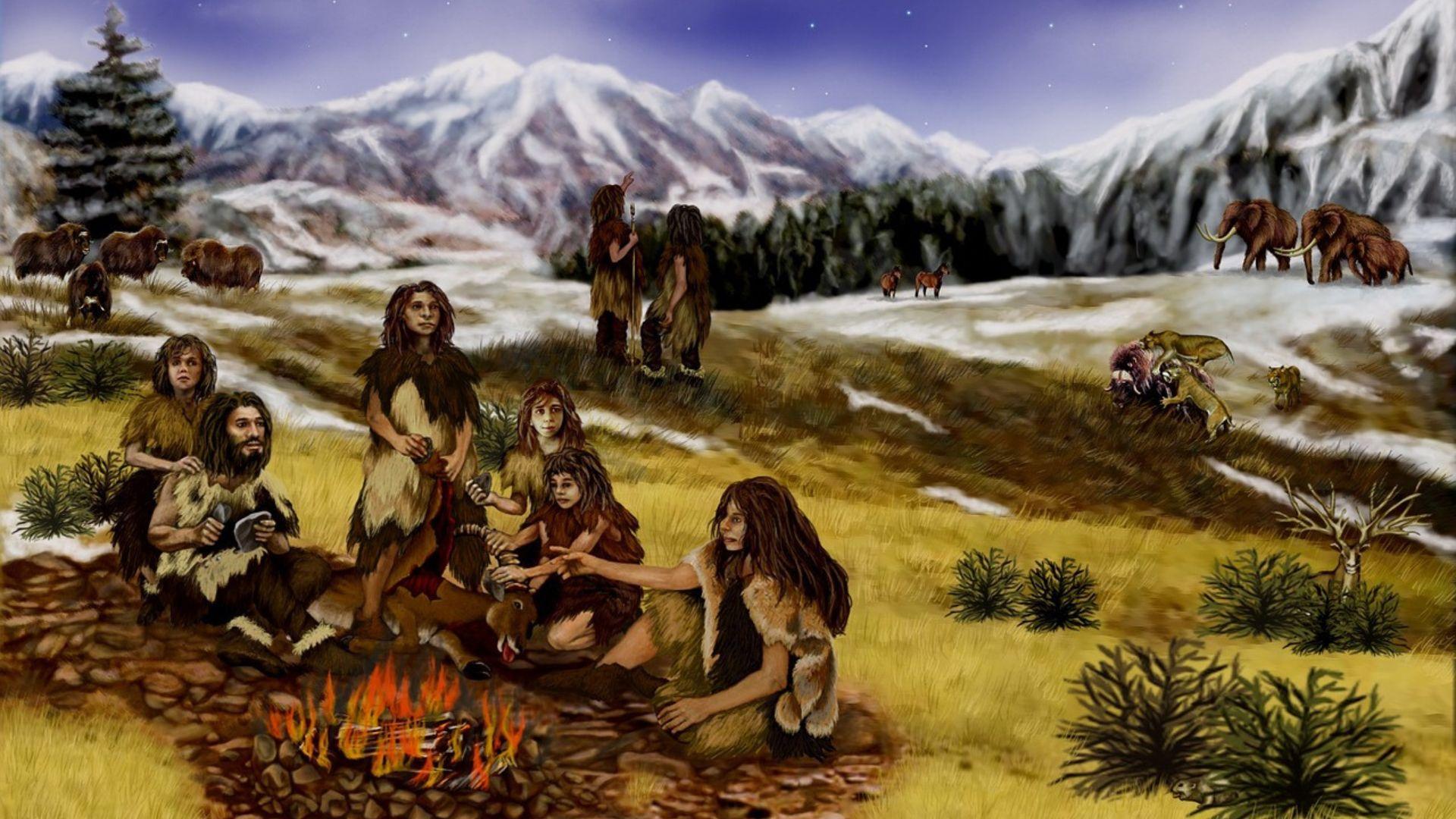
Stone tools in the ancient world had many uses, but Garba thinks that the chipped stone tools they found had a likely purpose. He thinks that it is likely they were used for cutting meat or scraping animal hides.

Source: 12019/Pixabay
Scraping an animal hide is important for stretching it out and getting rid of excess meat and fat that is still hanging on it.
Other Finds
While the researchers of this study think the tools are 1.4 million years old it’s possible that they are only merely 1 million years old.

Source: Jakub Hałun/Wikimedia
This would put ancient tools found in Spain at roughly the same age. The oldest tools currently on record date back to over 2.8 million years ago and were found in Eastern Africa.
Ancient Humans Got Around
This latest discovery really highlights that despite the lack of technology, ancient humans had the time and the drive to discover faraway lands. Rick Potts, the director of the Smithsonian Institution’s Human Origins Program, expressed his admiration for these ancient people.

Source: Jakub Hałun/Wikimedia Commons
“The oldest humans with this old stone tool technology were able to colonize everywhere from warm Iberia (Spain) to Ukraine, where it’s at least seasonally very cold – that’s an amazing level of adaptability,” said Potts.
