These 7 Possible Alien ‘Dyson Sphere’ Megastructures Could Save Earth’s Future
Researchers believe several stars within the Milky Way galaxy appear to harbor signs of advanced alien life in the form of a technological megastructure known as a Dyson Sphere.
If such a technologically advanced structure existed in our universe, the host civilizations would be considered far more advanced than our species on Earth. The new data has not only piqued the interest of researchers searching for extraterrestrial life in the depths of interstellar space but also holds the potential to significantly advance our understanding of the universe.
The Dyson Sphere
In the 60s, theoretical physicist Freeman Dyson was the first to propose the highly advanced Dyson Sphere. This structure would encompass a star and allow its host to harness unlimited energy until the star dies.

Source: Wikimedia/Wikimedia
“One should expect that, within a few thousand years of its entering the stage of industrial development, any intelligent species should be found occupying an artificial biosphere which completely surrounds its parent star,” wrote Dyson in a 1960 paper
Various Kinds of Dyson Spheres
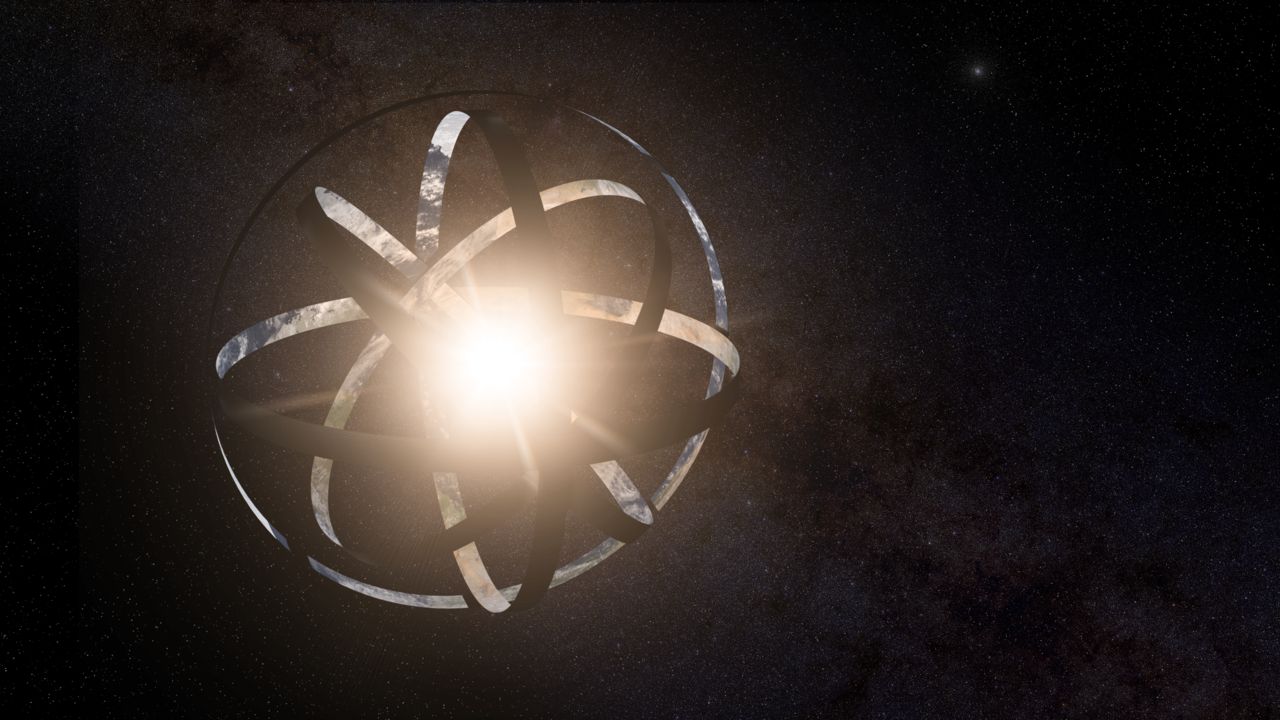
Dyson and researchers who have built upon his original idea have suggested there could be several forms of a Dyson Sphere.

Source: Wikimedia
The small versions would consist of ring stations and a gigantic mirror, whereas the largest would consist of a large sphere constructed around a star.
The Possibility of Spotting a Dyson Sphere in the Universe
Despite sounding like something from a science fiction novel, several scientists believe such a structure could exist. If it did, researchers suggest with considerable certainty that we would be able to spot it.

Source: Wikimedia
If a Dyson sphere encapsulated a star, it would heat up to extreme temperatures due to its close proximity to the celestial body. In turn, this would emit significant amounts of infrared radiation that astronomers could identify.
A Good Place to Look
One of Dyson’s six children, George, a technology writer and prominent author, explained how researchers may search for evidence of a Dyson sphere.

Source: Wikimedia
“Scientists (at the time) were largely receptive, not to the likelihood that alien civilizations would be found to exist, but that a search for waste heat would be a good place to look,” he said.
Seven Potential Stars With Dyson Spheres
During the era in which Dyson proposed his concept, the tools required to search for evidence of such did not exist. However, in the modern era, research groups such as the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory and the SETI Institute have the means to do so.

Source: Wikimedia
Researchers recently published a study that explored the depth of the Milky Way. They examined over 5 million stars to see if any showed signs of hosting Dyson spheres and discovered seven potential candidates.
Researchers Search For Dyson Sphere
The scientists, who published their findings in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, conducted their investigation to specifically search for the technologically advanced structures. They did so by looking for a particular form of infrared heat that could only be explained by something like a Dyson sphere.

Source: Freepik
In the wake of revealing their seven potential candidates, the researchers were met with considerable backlash from critics who’ve suggested alternative theories to their results.
The Tools Employed For the Search
The researchers began by using historical data gathered from telescopes that actively pick up infrared signatures and began searching for potential candidates that were located no further than 1,000 light years from Earth.

Source: Freepk
“We started with a sample of 5 million stars, and we applied filters to try to get rid of as much data contamination as possible,” said lead study author Matías Suazo.
Seven Candidates Emitting Infrared Light
These researchers, led by Suazo, a doctoral student in the Department of Physics and Astronomy of Uppsala University in Sweden, have meticulously conducted their study. They are confident that the seven candidates they have identified are indeed emitting infrared light, a crucial step in the search for Dyson Spheres.

Source: Wikimedia
“So far, we have seven sources that we know are glowing in the infrared, but we don’t know why, so they stand out,” she said.
More Likely to Be Dyson Swarms
“Dyson spheres are more likely to be Dyson swarms — a vast collection of solar-energy collecting satellites, each on independent orbits around the Sun,” Dr. Janna Levin told Salon.

Source: Wikimedia
“Any instrument that collects energy wastes some in the form of heat. It’s the heat signature that scientists have recently searched for. Heat signatures are so generic in nature that it’s far from a smoking gun and there are many possible natural explanations.”
Researchers Continue Looking For Answers
Speaking on the source of the infrared radiation coming from the stars, Suazo explained that researchers are still trying to figure out what causes it.

Source: Freepik
“It’s difficult for us to find an explanation for these sources, because we don’t have enough data to prove what is the real cause of the infrared glow,” he said.
The Source of Infrared Radiation
Nonetheless, researchers haven’t ruled out the possibility that the infrared radiation stems from Dyson spheres surrounding stars in deep space. However, they admit the critics are correct in suggesting it could be something else entirely.

Source: Wikimedia
“They could be Dyson spheres because they behave like our models predict, but they could be something else as well,” said Suazo.
Could Dyson Spheres Exist?
“My personal view is that, out of the nearly ~2 billion stars that Gaia has cataloged, there was an explicit search for, ‘Which objects are most consistent with the idea of this being a Dyson sphere?'” Siegel said.

Source: Freepik
“And these were the seven best candidates. None of them are particularly compelling — it’s just saying that if Dyson spheres are out there and have been built, could we find them and what is the best match, observationally, for that scenario.”
The Best Candidates
“They are the best Dyson sphere candidates we’ve come across so far, but this does not mean that they are Dyson spheres, or even that Dyson spheres represent the most likely explanation for the phenomenon we’re seeing,” Siegel said.

Source: Hopeful in NJ/Flickr
“Dust around a newborn star, a chance alignment with an infrared-bright background object, or dust due to some sort of rare cosmic catastrophe in the planetary systems of these stars (colliding planets or something similar) may also constitute viable explanations. “
Hot Planets
Dr. Ethan Siegle, an astrophysicist and science writer, believes that the stars that are emitting a larger amount of energy are not a result of the stars they are consuming. Instead, it is the temperature of the plant radiating off the planet’s surface.

Source: Ricardo Gomez Angel/Unsplash
“The larger the surface, the lower the temperature,” Siegel said to Salon. “So if you find a star emitting a large amount of energy but at a very low temperature, it makes sense to conclude that there’s either the star is very large and ‘puffy,’ or perhaps there’s an external structure around the star that’s radiating heat outward after absorbing the solar energy.”
The Next Step For Researchers
The researchers explained that they would conduct further studies on the seven-star candidates using a series of powerful instruments, including the James Webb Space Telescope.
Source: Wikimedia
Further investigations will allow scientists to take better readings in their search for potential stars that may well be encapsulated by a Dyson sphere. If they were able to find evidence of such, it could provide humans with proof that intelligent extraterrestrials exist somewhere in the depths of our universe.
Could Be Nothing
Siegle adds that these stars could be nothing exotic at all, saying: “Alternatively, it could just be normal old astrophysics at play, with no aliens, no megastructures, no Dyson spheres, and nothing exotic.”

Source: Wikimedia
“When you have an extraordinary explanation and a mundane explanation for the same observed phenomenon, you really need more (extraordinary) evidence to favor the former explanation over the latter one, and we don’t have that,” he added.
Unlikely to Be Anything Significant
Siegle is excited about the possibility of discovering Dyson stars for the first time, but doubts surround the discovery.

Source: Lucas Pezeta/Pexels
“Personally, I think these objects are very unlikely to be Dyson spheres,” Erik Zackrisson. an associate professor in astronomy at Uppsala University and one of the study co-authors said.
What Are These “Dyson Stars”
If these structures are not Dyson spheres, then what are they? “Some of them have already been argued to be due to chance alignments with background sources,” Zackrisson said.

Source: Pixabay/Pexels
“Such cases are astrophysically uninteresting, so my hope is that at least some of these sources will be confirmed to have intrinsic infrared excess fluxes — then we’re at least onto something interesting, even if it eventually boils down to extreme astrophysics rather than aliens.”
More Research Is Needed
These stellar anomalies are certainly thrilling, but scientists still need to conduct a significant amount of research to determine their causes. Unfortunately, it may take many years before we have conclusive evidence of Dyson Spheres.

Source: Freepik
“It’s important to keep an open mind, and it’s easy to understand why the most wild possibilities excite us,” Siegel said. “But without stronger evidence, this is just another example of people getting hyped up over what’s almost certainly going to be a big nothing-burger.”
Dyson Spheres Could Help Earth’s Future
Finding a Dyson sphere could prove that there is life beyond Earth, but it could also be beneficial as technology becomes a bigger constant in our day-to-day lives.

Source: Wikimedia
As humans grow in numbers and technological sophistication, generating more and more energy for our use will become essential to our survival. Finding a new source of renewable energy could be hugely beneficial.
Tapping Out
At some point, we will have tapped all available energy sources our planet has. So what do we do next?

Source: Lukas/Pexels
Because Dyson spheres draw energy from other planets, asteroids, and everything else in its solar system to collect the solar energy from a star, scientists believe finding and studying one of these spheres could give humanity insight into what we should do next.
Following the Law of Thermodynamics
Because of the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of the universe increases for a spontaneous process, a Dyson Sphere would necessarily radiate excess heat in the form of a strong infrared glow.

Source: Freepik
By focusing on finding IR radiation, Dyson suggests that we could be able to detect one of these civilizations in our galaxy.
The Challenges of Creating a Dyson Sphere
Constructing our own version of a Dyson sphere would be an enormous practical challenge for several reasons. Our civilization would need to dismantle an entire solar system to gather the necessary materials to build a man-made structure that could draw power from a star.

Source: Wikimedia
This would be decades to centuries away from our current technology as we are still trying to send (and receive) people from space.
