This Is an ‘Embarrassment’: White House Blasted for Opposing 19.5% Pay Increase for Junior Enlisted Troops
The military is currently experiencing a severe recruitment crisis, described as a “once in a generation” challenge. In response, a proposed 19.5% pay increase for junior enlisted troops has been put forward to help mitigate this issue.
However, the White House has expressed strong opposition to this proposal.
Veterans' Criticism
Veterans on Duty chairman Jeremy Hunt has been vocal about his disapproval of the White House’s stance.

Source: iStock
He argues that increasing pay is crucial for addressing the recruitment crisis and supporting troops who are struggling financially.
White House's Position
The White House has stated that it “strongly opposes” the significant, permanent change to the basic pay schedule before the completion of the Fourteenth Quadrennial Review of Military Compensation.

Source: Tabrez Syed/Unsplash
They assert their commitment to supporting service members but believe this change is premature.
Inflation and Financial Struggles
Since President Biden took office, inflation has risen by 20%, exacerbating the financial struggles of junior enlisted troops.

Source: Shutterstock
Hunt highlights that many of these service members live paycheck to paycheck, struggling to provide for their families amidst rising living costs.
Comparison to Student Loan Forgiveness
Hunt criticizes the administration’s decision to approve over $100 billion in student loan forgiveness while opposing the military pay raise.

Source: Freepic.diller, Freepik
He calls this disparity “truly remarkable” and argues that supporting the troops should be a priority.
Support from Lawmakers
Members of both parties in the House Armed Services Committee support the pay raise.

Source: Cytonn Photography/Pexels
Representative Adam Smith (D-Wash.) notes that the increase is essential for helping junior enlisted troops afford housing and improving recruitment and retention rates.
Recruitment Shortfalls
The Department of Defense reports significant recruitment shortfalls for the 2023 fiscal year: the Army missed its goal by 23.4%, the Navy by 19.8%, and the Air Force by 10.7%.

Source: Wikimedia
These figures convey a pretty significant sense of urgency in addressing pay and conditions for junior enlisted troops.
Impact on Recruitment and Retention
Increasing pay for junior enlisted troops is seen as a vital step to improve recruitment and retention.

Source: Freepik
Adequate compensation would — at the very least — make military service more inticing and help retain those already serving.
Hunt's Personal Experience
Hunt, a former platoon leader in the 3rd Infantry Division, shared that several of his soldiers struggled financially.

Source: Depositphotos
He emphasizes that this issue remains prevalent and needs urgent attention from lawmakers and the administration.
Broader Economic Context
The rising cost of living, particularly in housing, has put additional financial pressure on junior enlisted troops.

Source: Freepik
The proposed pay raise aims to alleviate these burdens and support service members in meeting their basic needs.
The Need for Immediate Action
Critics argue that waiting for the completion of the compensation review is not an option.

Source: Larry W. Smith/Getty Images
Immediate action is necessary to support troops and address the recruitment crisis effectively.
A Call to Prioritize Troops
The debate over the pay raise highlights a broader discussion about the nation’s priorities.

Source: Wikimedia
Ensuring that those who serve are adequately compensated and supported is crucial for maintaining a strong and effective military force.
Investing in the Future of the Military
“There is no investment more important than the one we make in the men and women who serve in our all-volunteer force,” House Armed Services Committee Chairman Mike Rogers, R-Ala., said in a statement after the bill passed.

Source: Karolina Grabowska/Pexels
He continued, saying, “We cannot kick the can down the road when it comes to providing for our service members.”
Improving the Quality of Life
“By improving the quality of life of our service members and their families, Democrats and Republicans in the committee sent a clear message: We are dedicated to recruiting and retaining the strongest, most diverse fighting force,” House Armed Services Committee ranking member Rep. Adam Smith, D-Wash.

Source: Brett Sayles/Pexels
The pay hike for E-1s through e-4s and a 4.5% raise for all service members will also help families as they can access more health care and child care.
Other Amendments Included in the Bill
The bill for a 19.5% pay raise is getting blasted in a culture war after House Republicans added amendments to roll back Pentagon policies on abortion and LGBTQ+ service members.

Source: Alex Green/Pexels
This is the second year in a row that the House has approved a version of the NDAA, which most party members use to target their ongoing agendas. While the original bill focuses on much-needed military quality-of-life improvements, the bill has been hijacked and opposed by the White House.
The Bill’s Ill-Intent
However, the bill had measures that many party members criticized as they targeted specific minority groups in the military.

Source: Somchai Kongkamsri/Pexels
“The adoption of poison pill amendments attacking reproductive health care, women, LGBTQ+ individuals, and people of color undermines the purpose of the defense bill by demeaning service members and degrading our national defense,” they said in the statement (via Military).
Pushing Back on Women’s Reproductive Rights
However, the bill passed in the House in a 217-199 vote. Among the amendments that Republicans approved could reverse the Pentagon’s year-one policy of covering leave and travel for service members seeking abortions.

Source: Rosemary Ketchum/Pexels
This measure comes two years after Roe v. Wade was controversially overturned by the US Supreme Court.
Removing Health Care for Transgender Military Persons
Another amendment that was approved in the bill was to bar the Pentagon from covering gender-affirmation health care for transgender troops and their dependents.
Source: Win McNamee/Getty Images
Currently, the government provides a health care program for service members, retirees, and their families worldwide to help provide comprehensive coverage, health plans, special programs, prescriptions, and dental plans.
Targeting Diversity Initiatives
Republicans also targeted diversity initiatives that have been introduced into the military like the DEI, which ensures commanders and leaders are being inclusive in their decisions, actions, and admissions which provide equal opportunities and access to all.

Source: Sharefaith Sharefaith/Pexels
However, Republicans in the House passed amendments that would eliminate any military diversity office, fire the program’s staff, and institute a permanent hiring freeze on diversity-related jobs.
Proposing to Bring Back a Confederate Memorial
There was one area where conservative lawmakers fell short. The bill proposed putting back the Confederate memorial that was removed from Arlington National Cemetery last year.
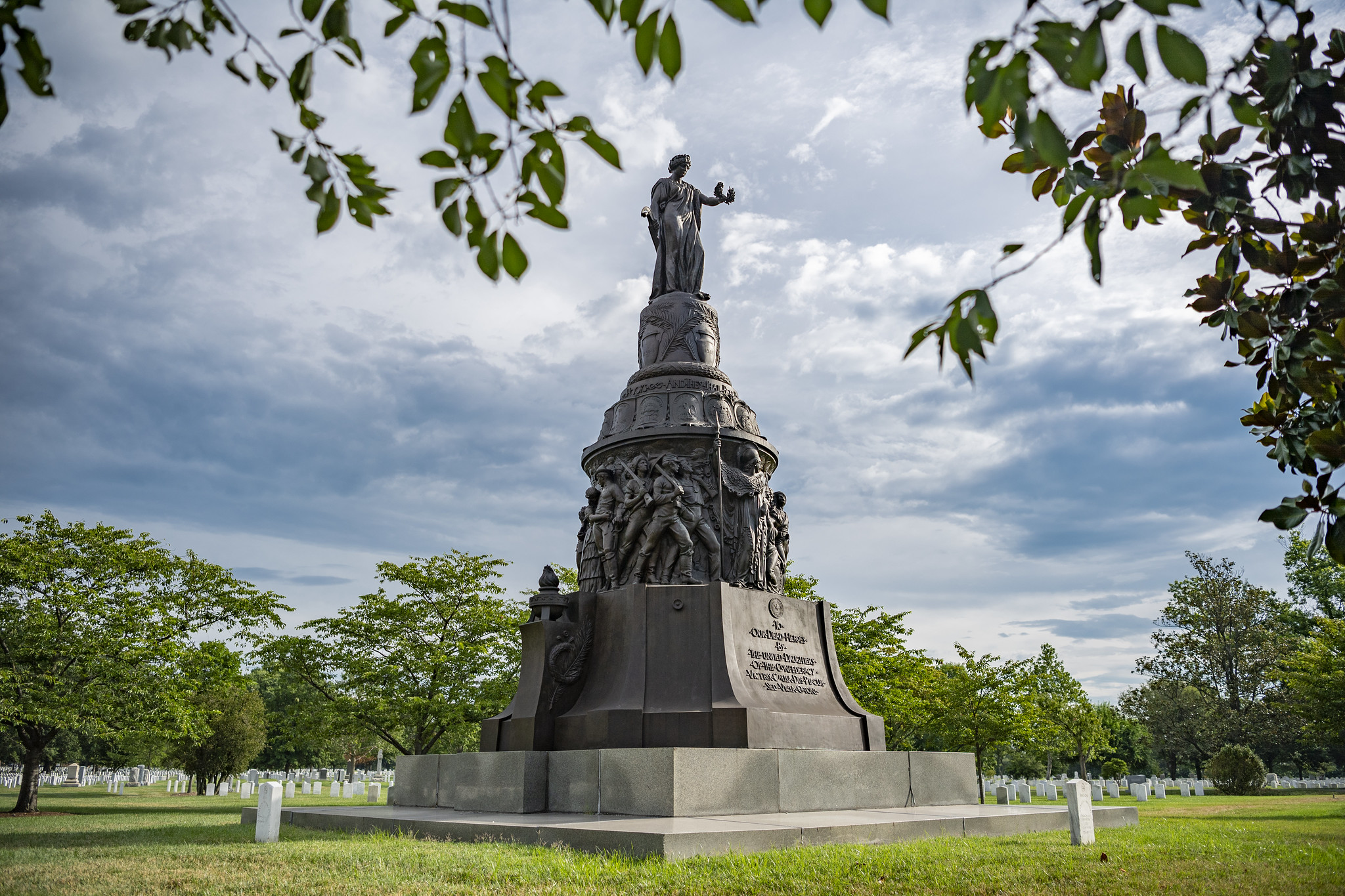

Source: Arlington National Cemetery
The Confederate monument was removed after a national campaign gained momentum after the murder of George Floyd and the destruction of several monuments by protesters.
Moving Up to the Senate
All of these amendments – both proposed, passed, and opposed – had largely been discussed and negotiated with the Democrat-controlled Senate. The most controversial measures were scrapped from the final bill that became law.

Source: Freepik
The most divisive amendments were not included in the bill advanced by the Senate Armed Service Committee this week. “My gut tells me that the final bill will look a little bit more like the Senate version than the House version,” Sen. Tim Kaine, D-Va., said.
Increasing the Military Budget
During debates about its NDAA, the Senate Armed Services Committee approved an amendment from Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss., that endorses a $25 billion increase to the defense budget.

Source: Freepik
This increase will add to the Biden administration’s request for fiscal 2025 and the level required under budget caps approved by Congress last year.
Currently Military Budget
According to USA Facts, the Department of Defense (DoD) requested $842 billion for 2024, which helped the DoD support the world’s third-largest military with nearly 1.3 million active-duty troops.

Source: Somchai Kongkamsri/Pexels
How the money is spent on each military department is clarified each year in the defense budget, which is shared with the public.
Why Some Voted Against the Bill
However, some of the amendments proposed threaten to break laws. “I regret that I needed to vote against passage of this bill because it includes a funding increase that cannot be appropriated without breaking lawful spending caps and causing unintended harm to our military,” Reed said in a statement.

Source: Monstera Productio/Pexels
“I appreciate the need for greater defense spending to ensure our national security, but I cannot support this approach.”
